This post was written by Colin Goebel, human performance specialist, Parkview Sports Medicine.
While not the only measure of fitness, VO2 max can be a strong indicator of how efficiently your body responds to movement or physical demand. A higher number can mean higher energy availability. It’s helpful to have a more detailed understanding of how VO2 max is measured and how it can be improved.
What is VO2 max?
In the simplest terms, VO2 max is the maximum amount of oxygen your body can use as a fuel source for exercise. The body has two types of energy systems: aerobic and anaerobic. Anaerobic energy system, without the use of oxygen, is typically used in short, high intensity movements (sprinting, jumping). The aerobic system, with the use of oxygen, is typically used in lower intensity exercises for long durations of time (walking, jogging). VO2 max is a representation of how effective the aerobic system is in providing fuel for exercise.
How is VO2 max tested?
The most accurate VO2 max test is completed on a treadmill in a laboratory. The test typically involves completing an 8–12-minute run with the intensity gradually increasing until the runner’s oxygen consumption level plateaus. The runner’s oxygen consumption level is monitored via a facemask, where measurements are taken of oxygen inhaled and carbon dioxide exhaled.
An easy way to estimate VO2 max at home is to use the equation:
- Calculate resting heart rate (measure your pulse for 20 seconds and multiply the number by 3)
- Calculate maximum heart rate (220 minus your age)
- Divide your maximum heart rate by your resting heart rate and multiply the number by 15.3
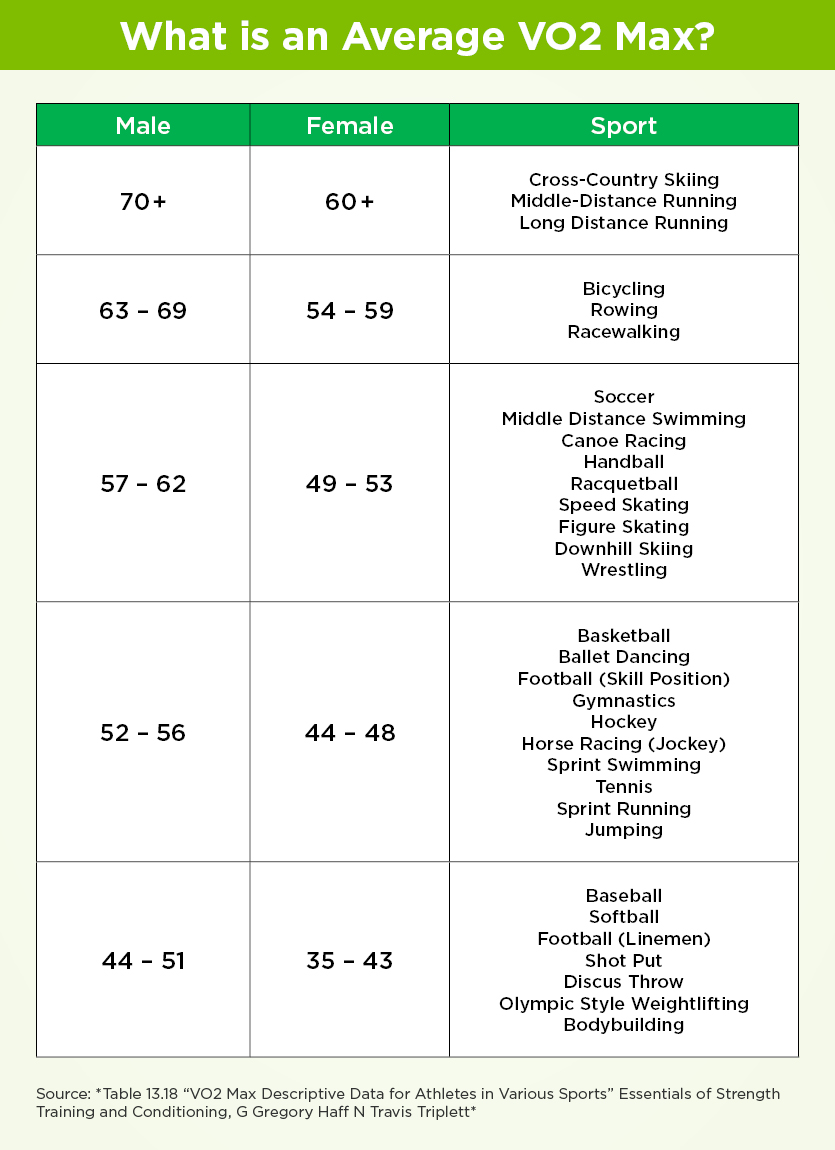
What is an average VO2 max?
*
How to improve VO2 max
The approach to improving VO2 max can differ between beginners and more advanced athletes. Beginners can improve VO2 max with consistent aerobic training. This can include running, swimming, cycling, rowing, etc. for a longer period of time at a relatively low intensity. More advanced athletes can use the same exercises; however, the more advanced athletes will need a higher intensity. Interval training can be specifically beneficial in improving VO2 max by allowing an increase in intensity for a shorter period of time.
*Table 13.18 “VO2 Max Descriptive Data for Athletes in Various Sports” Essentials of Strength Training and Conditioning, G Gregory Haff N Travis Triplett*



